usp class vi vs iso 10993
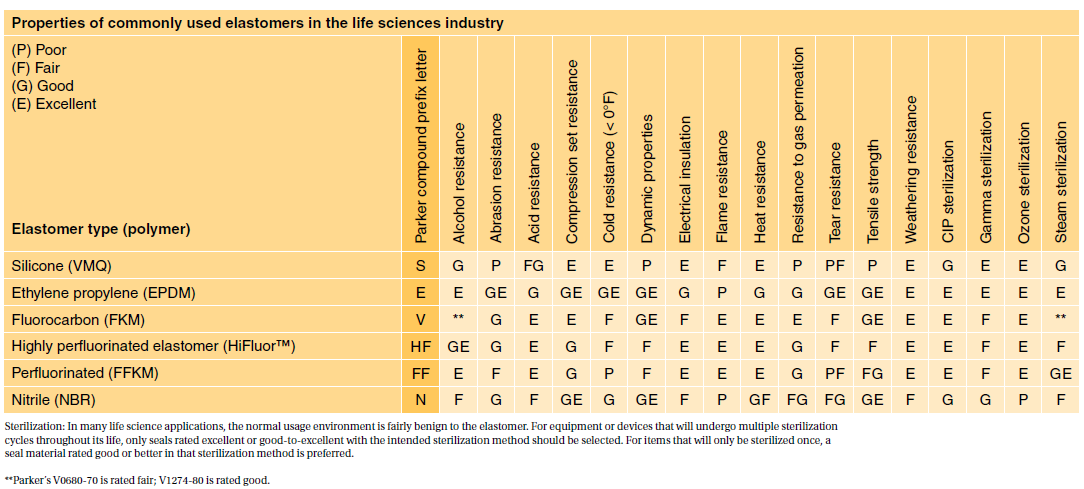
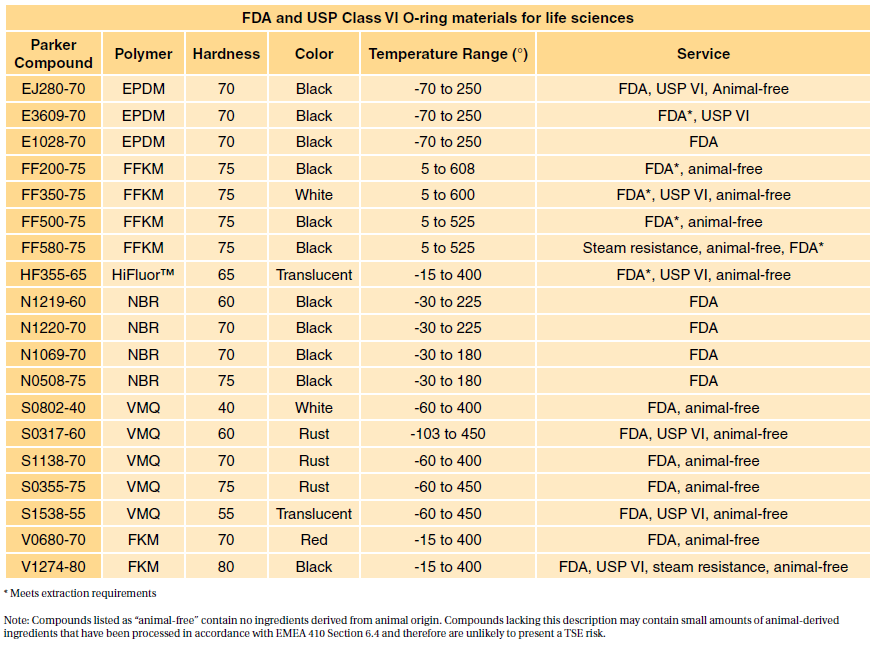
Take an ASTM D2000 call out. Meets USP Class VI and ISO 10993-5 cytotoxicity testing requirements.
Biocompatibility Of Plastics Zeus
Predictable Safe and Stable.

. Glass transition temperature of more than 140C. USP Class VI vs. We carry a wide range of materials from the worlds top medical resin suppliers including USP Class VI and ISO 10993 certified biocompatible resins with full FDA Master File support.
This post will take a deeper look at what biocompatibility is and how it is defined by the International Standards Organization. In 1995 the FDA adopted ISO 10993 as its biocompatibility approach. Serviceable from -60F to 450F.
Depending on the devices use the sterilization process might obligate you to do ISO 10993. Meets USP Class VI requirements and passes ISO 10993-5 tests for cytotoxicity. A more rigorous standard for the biological evaluation of medical devices is ISO-10993.
Parylenes thickness is critically controlled and extremely consistent. USP Class VI demands an intracutaneous irritation test. A selection of Figure 4 VisiJet Accura and DuraForm plastic materials have met the requirements of ISO 10993-5 -10 or USP Class VI testing.
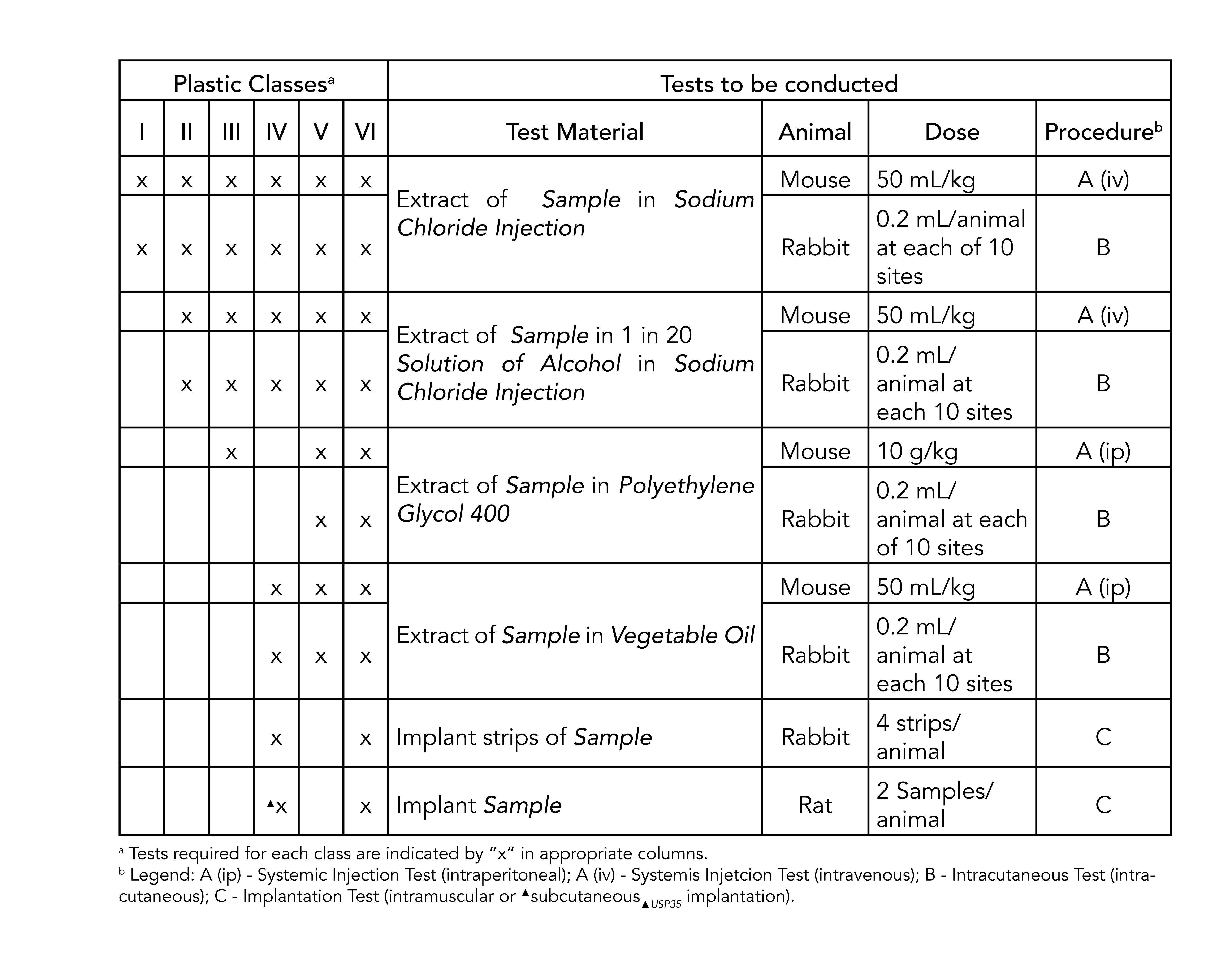
In fact USP Class VI has been largely superseded since the release of ISO 10993 in 1995. A rubber compound has set physical parameters it needs to meet. Systemic injection test Intracutaneous test Implantation test USP standards for the first two tests in the list above are nearly identical to ISO-10993 standards for.
It is transparent pin-hole free and conforms precisely to any surfaces features. Biological evaluation of medical devices Part 1. That said the lack of risk assessment in USP Class VI can be a problem.
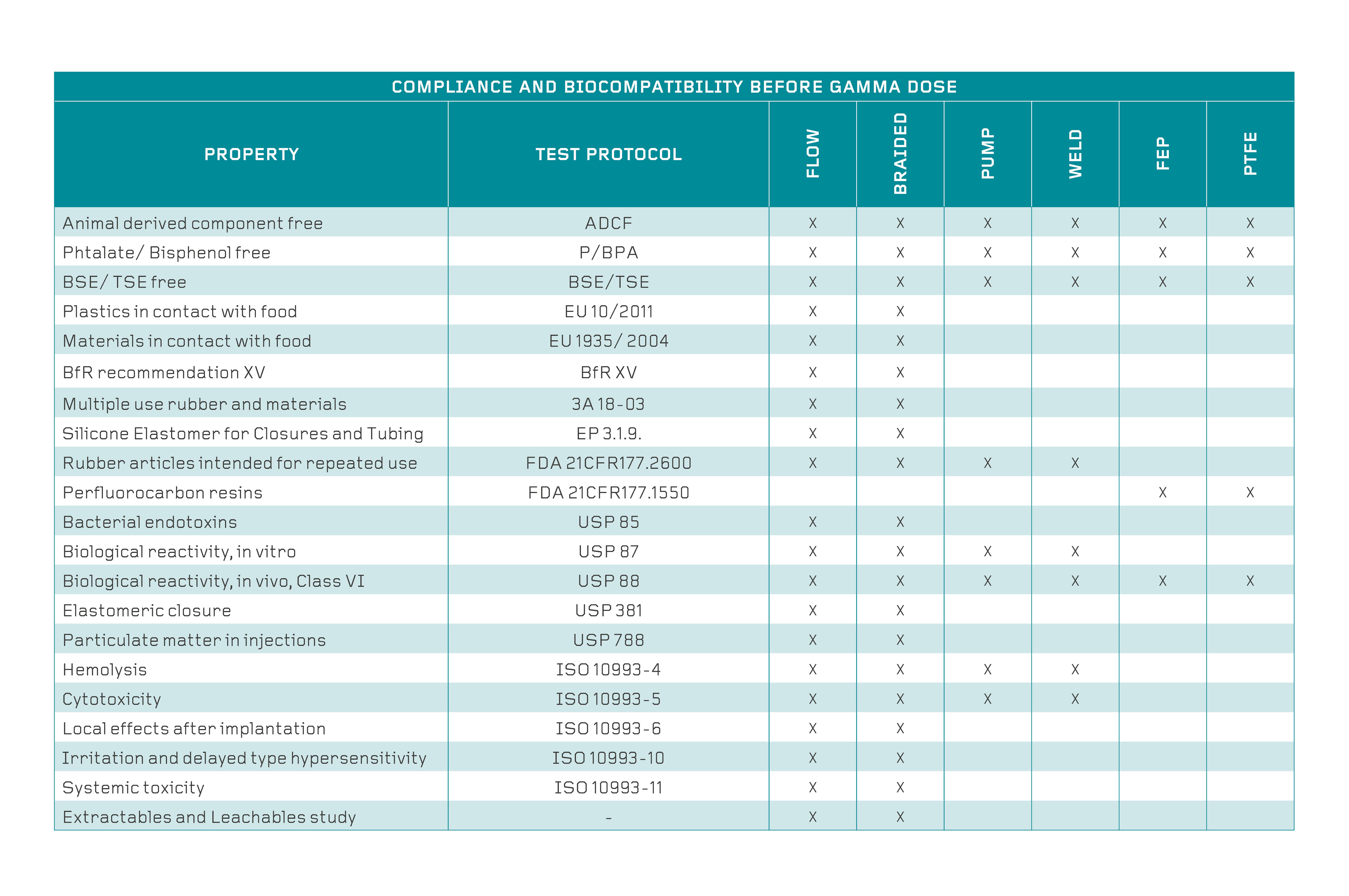
Though not a limited series of tests some biocompatibility requirements for medical devices may exceed the testing performed in USP Class VI. Typically the terms USP Class VI or ISO 10993 materials are used. Up-to-date materials manufacturers provide both USP and ISO 10993 test data to support both pharma and device customers.
While it is possible a USP Class VI material could also be ISO 10993 compliant its not a given and USP Class VI alone is not sufficient for adherence to ISO 10993. This is their current stance today. In 1988 in vitro tests were explored and USP concluded that in vitro.
However Class VI also requires subacute toxicity and implantation effects which many ISO 10993 categories do not. Biocompatibility testing biocompatible materials biocompatible rubber ISO 10993 medical molder medical molding medical silicones USP Class VI. If yes to the first question then USP Class VI is not a relevant qualification for it.
A number of our plastic materials are ISO-10993 or USP Class VI capable. Class VI and ISO 10993 are recommendations for testing based on the use of the final device. Parylene has a long history of use as a protective coating for medical device biocompatibility and conforms to the USP Class VI and ISO 10993 standards.
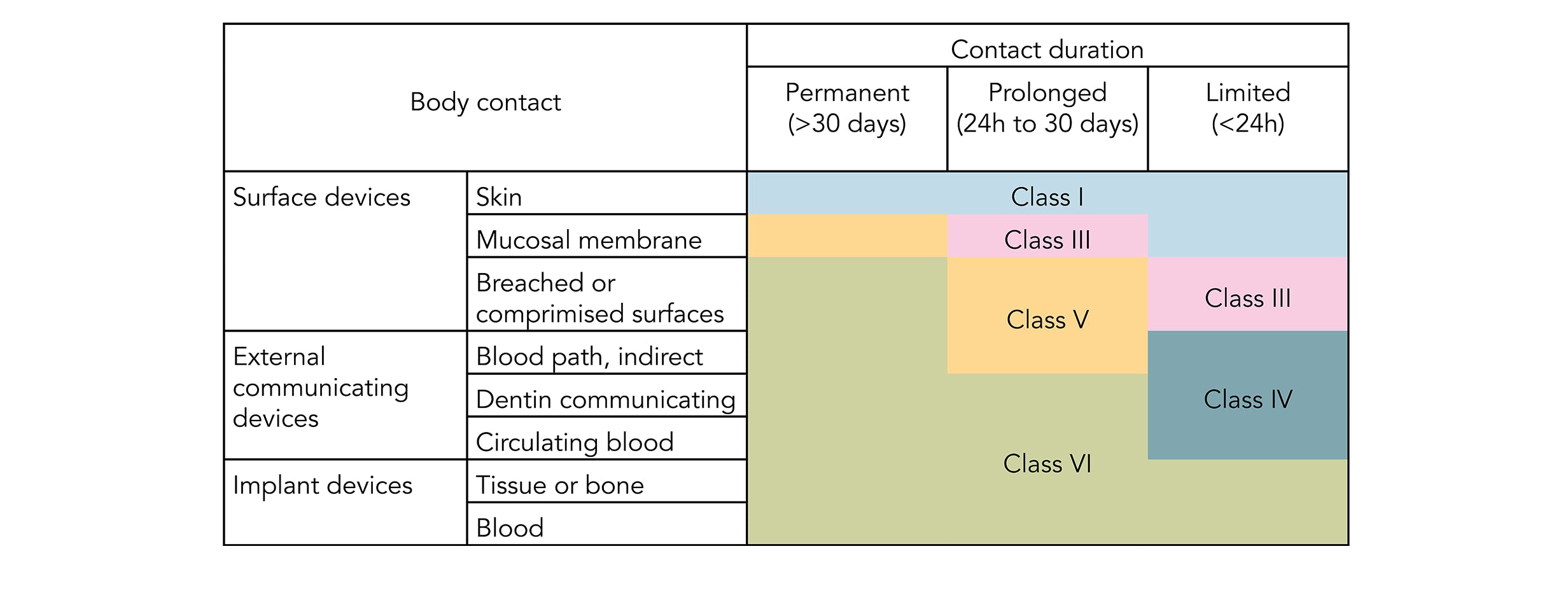
The materials listed below are ideal for. Testing is commonly done as per USP which requires three types of. Plastics were assigned Class I-VI based on the biological in vivo testing systemic injection intra-cutaneous and implantation tests.
You might establish biocompatibility via making the device of a Recognized Consensus Standard material using a validated process that does not degrade that material or by ISO 10993 testing. Our portfolio approach offers the most expansive selection of medical resin materials in the industry balancing performance cost reliability. Duration similar to ISO-10993 and each class has a different set of testing requirements.
The most stringent Class VI requires three types of tests. USP Class VI. The guidance memo wasis G95-1.
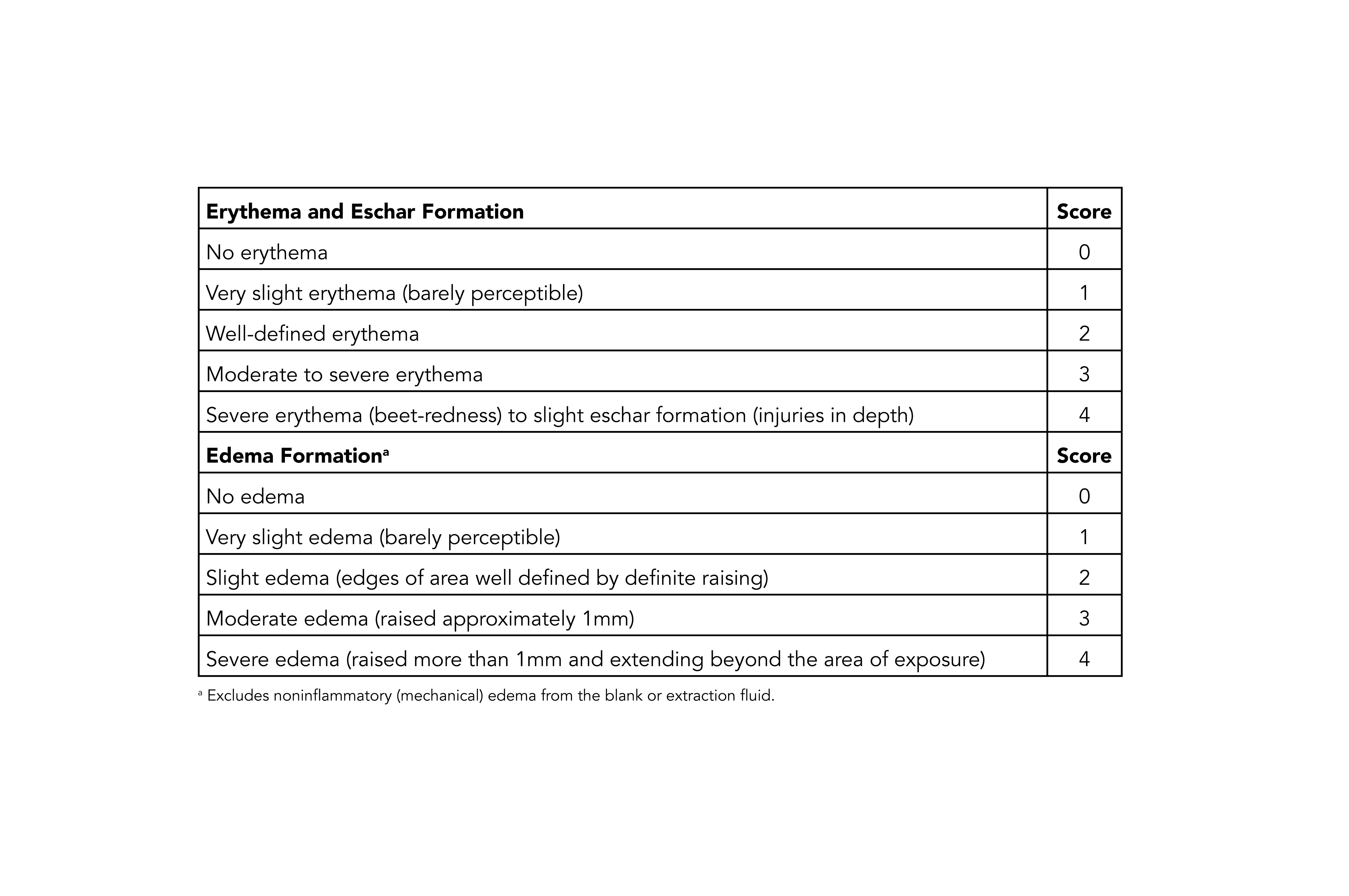
1965 USP XVII introduced Biological TestsPlastics Containers section was added and made official in the Compendium. USP Class VI Regiment Irritation Systemic Injection Implantation 1 week Biological Evaluation Plan BEP. To begin let us address just what biocompatibility is.
A more rigorous standard for the biological evaluation of medical devices is ISO-10993. 3D printing of one day crown prep guides. Most applications are fairly benign to elastomers.
ISO-10993 is a standard that utilizes systemic toxicity and intracutaneous reactivity testing. For this reason the FDA provides a standard 21 CFR1772600 defining allowable rubber compound ingredients and extractibles based on toxicity and carcinogenicity. USP class qualification no longer plays any role in medical device materials evaluation.
USP Class VI Testing is only one standard of biocompatibility however. Sealable and weldable either pre- or post-sterilization C-Flex 072 provides prolonged pump life Sterilizable by gamma irradiation and autoclave Product Validation Test Summaries available upon request Moldable bondable and formable for single-use assemblies and overmolds Temperature. USP Class VI ISO 10993-5 Cytotoxicity In-Vitro Features Benefi ts.
It depends to a large extent on the application and therefore also on the application period of the finished product. So does ISO 10993. Though not a limited series of tests some biocompatibility requirements for medical devices may exceed the testing performed in USP Class VI.
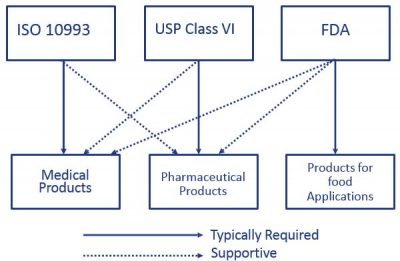
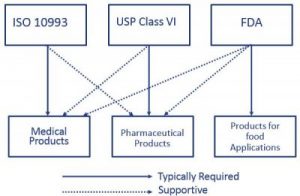
For most patient-contact applications a material that meets US Pharmacopeia USP Class VI andor ISO 109933 will be required. 3D printing of dental and orthopedic surgical guides. Evaluation and testing within a risk management process.
That being said if you cant get an ISO 10993 compliant material often because the material simply hasnt been tested using a USP Class VI material is a less risky option. Then you need to understand the differences between ISO 10993 and USP Class VI and the nature of each standard. Many medical device companies are familiar with USP Class VI but that standard isnt as strict as ISO 10993.
In fact USP Class VI is sometimes seen as a minimum requirement for biocompatibility. Medical Silicone Rubber Molding and Silicone Rubber Mold Materials. Unlike other rubber standards theres no one standard that engineers use for an approval.
ISO 10993 is designed for medical products that remain permanently or for a very long time in the human body so for shorter applications a USP Class VI or even a lower USP Class certification is often sufficient. USP Class VI testing is conducted by producing an extract of the product with different extraction fluids such as polyethylene glycol and vegetable oil and injecting it in specimen rabbits and mice in vivo alive to observe the biological response to the extract. Rapid curing no mix system.

Iso 10993 Vs Usp Class Vi Medical Molding And Bicompatible Rubber The Rubber Group

Understanding Food Grade Vs Biocompatibility For Medical Device Materials Medical Product Outsourcing
Biocompatibility Of Plastics Zeus
Material Selection Medical Injection Molding Xcentric Mold

Usp Class Vi Foster Corporation
Biocompatibility Of Plastics Zeus

What Is Iso 10993 How Is It Different From Usp Class Vi Ppt Download
Material Selection Medical Injection Molding Xcentric Mold

Understanding Food Grade Vs Biocompatibility For Medical Device Materials Medical Product Outsourcing
Brilliant Mind The World Of Tubing For Medical Use Medical Plastics News